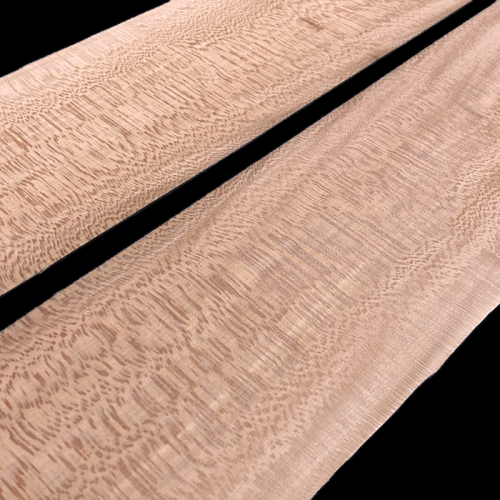
Flaky Planewood Veneers 350 x 22 cm
Flaky Planewood Veneers 350 x 22 cm
Genuine wood sliced-veneer sheets, in sequence.
Length: 350 cm.
Width: 22 cm.
Thickness: 0.6 mm.
Sold by the sheet.
These photos are taken from the veneer sheets you will receive.
Flaky Planewood Veneers 350 x 22 cm
Genuine wood sliced-veneer sheets, in sequence.
Dimensions:
Length: 350 cm.
Width: 22 cm.
Thickness: 0.6 mm.
Measurement scaling:
The width is rounded to the covered centimeter. For example, 15.8 cm is given 15 cm.
The length is rounded to 5 centimeters. For example, 257 cm is given 255 cm.
Pictures:
These photos are taken from the veneer sheets you will receive.
While we strive to capture the color as accurately as possible, please note that the color may vary slightly from the photo. The screen on which the photos are viewed can also affect their appearance.
What is Planewood?
What are the common names for Plane trees?
Plane, Platanus, Common Plane, Maple-leaved Plane, London Plane, European Lacewood.
Do not confuse with the Maple plane leaves or False Plane Maple (Sycamore).
What is the botanical name of the Plane tree?
Platanus x acerifolia.
What is the origin of the Plane tree?
The Common Plane is found throughout Europe, from England in the North to Greece in the South.
It is an ornamental tree placed in parks, squares, and streets, providing appreciated summer shade.
However, it is also an alignment tree planted along roads by Napoleon. In addition to providing shade, it helps slow invaders by felling trees on the road.
How do you recognize Planewood?
The first thing that stands out is its flakes; whether thin or big, they are omnipresent. Indeed, plane wood is sought after for its flakes, as it offers graphic light effects.
Its color ranges from medium pink of its hardwood to white-yellow of its sapwood. Some old woods have developed a heartwood color with brown/greenish veins.
What are the mechanical properties of Planewood?
Weight: approximately 675 kg/m³ at 10-12% moisture content.
Janka hardness: 4180 Newtons; for comparison, Ash is at 6580 N and Poplar at 1650 N.
Elasticity: 8.90 GigaPascals; for comparison, US Maple is 12.62 GPa, and Poplar is 9.75 GPa.
Breaking strength: 74 MegaPascals; for comparison, US Maple is 109 MPa, and Poplar is 62 MPa.
What are the uses of Planewood?
Plane wood is used in cabinetry, high-end decoration, and guitar making.
Plane wood is less sensitive to humidity than beech for carpentry, but xylophagous insects particularly appreciate it if it has not been previously steamed.
Note:
Among prestigious creations that used planewood, the legend is that the Trojan Horse was made from Planewood.
What are Wood Veneers?
Veneers are thin sheets of wood obtained by slicing or peeling.
Their surface has the appearance of planed wood without any finish or treatment. They are neither glued nor backed with any other material. This means that both faces of the sheets can be used.
Wood Veneers are mainly used to cover less aesthetic substrates such as plywood or particleboard to make furniture or wall panels.
Veneers are also used to create decorative objects such as lamps, jewelry, bookmarks, and more.
By assembling several sheets of veneer on top of each other, it is possible to manufacture objects requiring high mechanical resistance, such as skis, bicycle frames, or musical instruments.
The applications of veneer are as varied as they are multiple.
Since veneers are genuine wood, all wood finishing products, such as varnish, stain, or oil, are suitable. The choice of finish will depend on your personal preferences and the object's final use.
The veneer offered here is a sliced sheet of uniform thickness, but the thickness might differ from one species to another. The standard thickness is around 0.6 mm.
Although the edges of the veneers have been cut roughly straight, they are not perfectly parallel. Some veneers may retain the natural taper of the tree, being slightly wider at the foot than at the top.
Some veneers may have a trace of a waney edge (an edge following the tree's natural shape) on the sides. In this case, the dimensions indicated correspond to the minimum width of the veneer, as specified in the "Dimensions" paragraph.
How to use veneers?
How to cut the veneers?
Veneers can be easily cut with a utility knife.
For straight cuts, the best results are obtained with a veneer saw.
Use a fretsaw, scalpel, or veneer knife for curved cuts.
Always allow for a slightly larger veneer sheet than your intended surface. This will allow you to adjust the size after gluing for a clean finish.
A flush trimmer can also be used to trim the veneer after gluing.
When cutting with a utility knife or veneer knife, it is best to cut with the grain of the wood. To check this, run your finger along the edge of the sheet. The direction that feels smoothest is the ideal direction for cutting.
What is veneer splicing?
As the veneers have the width that nature gave us, you might need to cover an area wider than the veneers available.
Therefore, you need to splice the veneers by gluing or fixing them, side by side, with tape to obtain the desired width.
Trim the veneer's edges with a straight and smooth cut to realize good jointing.
Stick the veneers with tape (the blue one is a good choice.)
Usually, the veneers are spliced side by side, but they can also be spliced foot by foot to obtain a longer length.
The splicing must be done before gluing the veneers on the substrate.
What Glue to Use for Veneering?
Several types of gluing are possible.
Vinylic glue (PVA or PVB) is well adapted to porous substrates such as plywood, particle board, or MDF. The veneers must be pressed with clamps over the entire surface at once.
Note: Veneers can also be glued using vinylic glue and iron, but we strongly recommend this technique only if other gluing solutions are impossible.
- Neoprene glue is applied to all surfaces, especially non-porous surfaces, using two coats of glue and marouflage.
- Animal glue, such as hide, sinew, or bone glue, are pellets that must be cooked in a double boiler and used hot.
How to Sand Veneers?
Veneers and all our products are genuine wood and can be sanded according to thickness.
Please do not use a belt sander, regardless of the veneer's thickness, as it could pierce it.
With a 0.6 mm veneer, lightly sand with 120 grit and then finish with 180 or 240 grit. With an orbital sander, 180 grit is already sufficient for most applications.
How to Finish a Veneer Realization?
All finishing products generally used for wood are suitable for finishing our products. For example, you can use a varnish, wax, paint, or oil.
However, ensure that the product you want to use is compatible with the final use of your creation.
More information:
Please look at our TUTORIALS; you might find some valuable tips.
Please contact us by email or phone for any additional information.
Data sheet
- Species
- Planetree
- Thickness group
- Standard
- Grade
- Quarter-cut
You might also like
 English
English